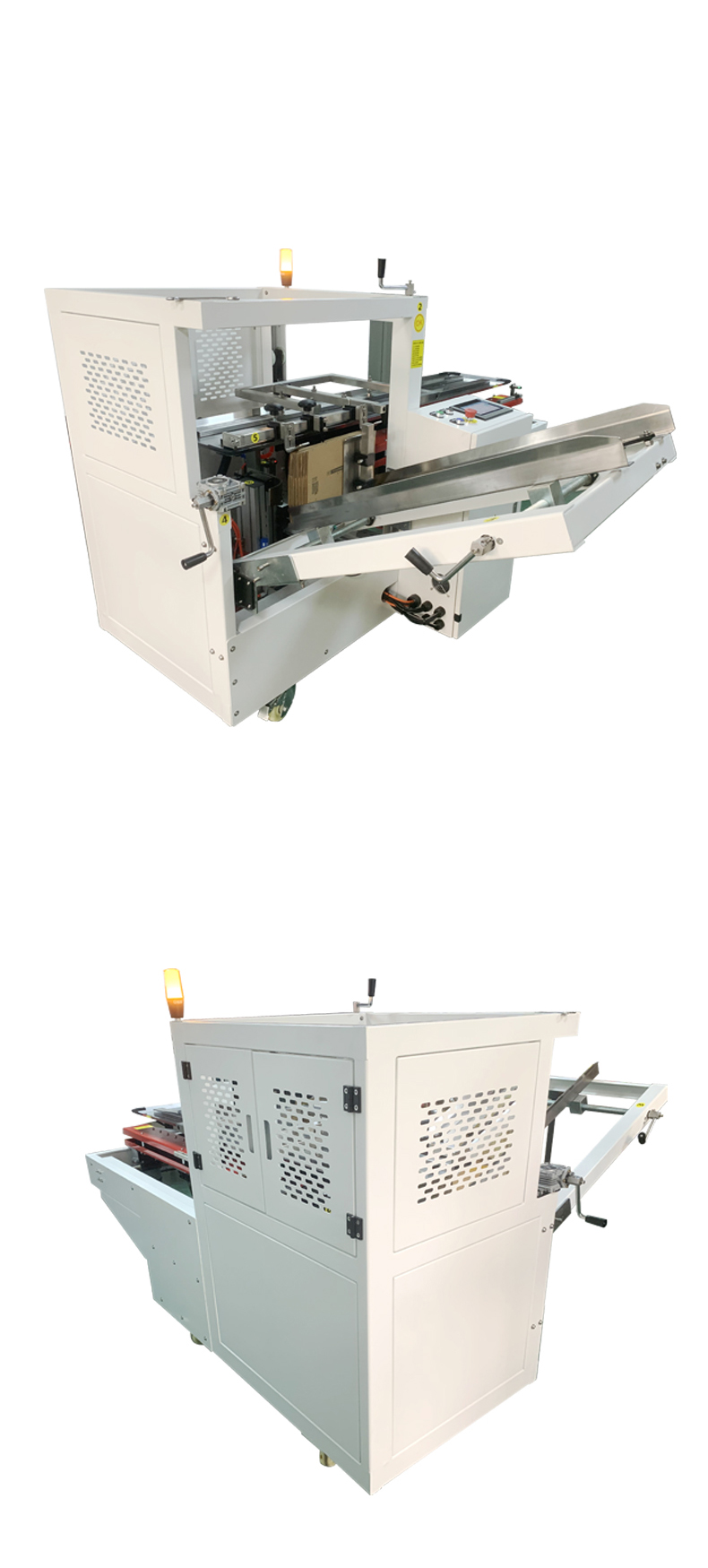
The operational process of an automatic carton opening and bottom-sealing machine typically includes core steps such as equipment debugging, carton loading, automatic carton opening, bottom folding, sealing operations, and finished product output. The specific steps are as follows:
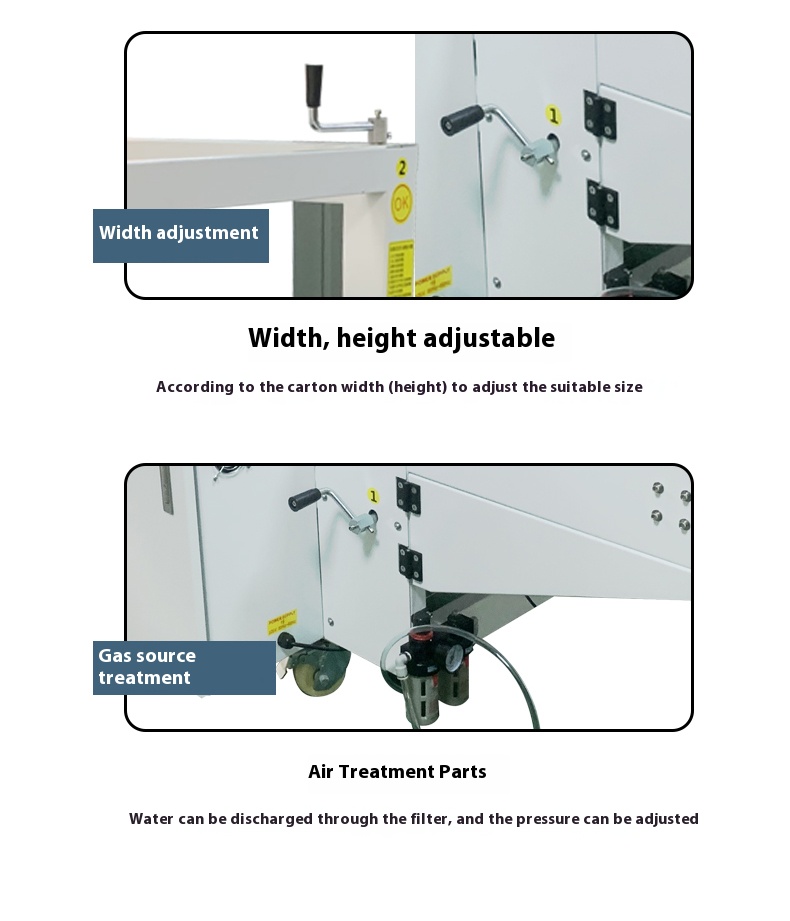
- Adjust the position of the guide plates, the width of the forming frame, and the parameters of the flap folding mechanism according to the size (length, width, height) of the carton to be processed, ensuring the carton can be accurately unfolded and folded.
Example: For a carton with dimensions of 500mm (length) × 300mm (width) × 200mm (height), input the corresponding parameters via the touchscreen or call up the stored preset value "500×300×200".
- Select the sealing type (tape, hot-melt adhesive, or stapling), install the corresponding consumables (e.g., tape rolls, hot-melt adhesive sticks, or U-shaped staples), and adjust the sealing position (e.g., center or edge of the bottom).
- Start the equipment for idling, observe the smooth operation of components such as the robotic arm, suction cup, and conveyor belt, and confirm no jamming or abnormal noise before entering formal production.
- Neatly stack flat cartons in the equipment's magazine (usually top or side loading), ensuring consistent orientation (uniform printing side or folding direction).
- The vacuum suction cup or mechanical claw automatically descends to pick up the top carton, which is then transported to the carton opening station via a conveyor belt or robotic arm.
- When the carton is transported to the forming frame, the mechanical arms or baffles on both sides simultaneously expand the left and right side panels of the carton, followed by the front and rear baffles pushing to unfold the bottom, forming a complete rectangular box.
- Some equipment is equipped with photoelectric sensors to detect whether the carton is fully unfolded, automatically adjusting or alarming if not in place.
- The front, rear, left, and right flaps (folding edges) at the bottom of the carton are sequentially folded into place by the folding mechanism:
- First fold the left and right side flaps, then the front and rear main flaps (the order may vary for some equipment), ensuring the bottom is flat and aligned.
- During folding, the pressing device simultaneously compacts the flaps to avoid misalignment.
- Tape Application: The tape roll is unwound through guide rollers. After the bottom flaps of the carton are folded, the tape cutting device automatically sticks the tape to the bottom seam and cuts off the excess tape.
- Application Scenarios: Suitable for ordinary cartons and medium-load requirements, with low cost and easy tape replacement.
- Gluing and Bonding: The hot-melt adhesive machine heats the adhesive stick to a liquid state and sprays it evenly onto the folded flap seams through a nozzle. The pressing roller then compresses the flaps to quickly cure and bond the adhesive.
- Application Scenarios: Ideal for high-speed production lines and scenarios requiring high-strength sealing (e.g., heavy-duty packaging), with a firm adhesive layer and resistance to cracking.
- U-Shaped Staple Fixing: The stapling mechanism drives U-shaped staples into the overlapping area of the bottom flaps, typically used for heavy-duty cartons (e.g., industrial equipment packaging) with strong load-bearing capacity.
- Precautions: Regularly check the staple quantity in the magazine to avoid sealing failures due to staple shortages.
- The sealed carton is transported via a conveyor belt to the next process (e.g., manual loading, automatic filling machine, or carton sealer). Some equipment supports intelligent docking with the production line (e.g., identifying carton specifications via barcode scanning).
- High-end equipment is equipped with a visual inspection system that captures images of the bottom seal through cameras to automatically identify defects such as skewed tape, insufficient adhesive, or misaligned staples. Unqualified products are rejected or marked.
- Manual Sampling: Regularly inspect the sealing firmness of finished cartons (e.g., test load-bearing capacity by lifting the carton slightly) to ensure compliance with packaging standards.
- Do not reach into the moving areas of robotic arms or suction cups during equipment operation. Press the emergency stop button to interrupt operation in case of emergencies.
- For hot-melt adhesive equipment, avoid contact with high-temperature components (e.g., glue gun nozzles) to prevent burns.
- When the tape is exhausted, replace it with a roll of the same specification as prompted and adjust the tape tension; hot-melt adhesive sticks require preheating (usually 5-10 minutes).
- In case of carton jamming or incomplete flap folding, the equipment will automatically alarm and stop. Operators should clear the jammed carton and adjust the folding mechanism as prompted by the touchscreen before restarting.